
Headache - Understanding Causes, Types, and Relief Strategies
Introduction:
Millions of people all over the world struggle with headaches, a common but complex health issue. The term "headache" encompasses a range of problems ranging from mild, rare headaches to severe, debilitating migraines. Understanding the types of headaches, their causes, and how to best manage them is important for those seeking relief. In this blog post, we’ll explore various aspects of headaches, including their symptoms, triggers, and treatment options to relieve your pain and improve your overall quality of life.Section 1: Types of Headaches
[caption id="attachment_23901" align="alignnone" width="940"] Different Types of headache.Fig.1.o[/caption]
Different Types of headache.Fig.1.o[/caption]
1.1 : Tension headaches
Migraines is a type of headache characterised by recurrent mild to severe headaches, which are often accompanied by other symptoms such as sensitivity to light, sound, or smell, nausea and vomiting Migraine can cause biting disabled and can last for hours or even days.
There are two main types of migraine: migraine with aura and migraine without aura. An aura is a set of neurological symptoms that occur before or during a migraine attack, such as blurred vision, numbness in the face or hands, or difficulty speaking The exact cause of migraine is not well understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some triggers that can cause a migraine include stress, certain foods or drinks, hormonal changes, lack of sleep, weather or changes in air pressure Treatment of the common cold may include preventive measures and aggressive treatment to reduce symptoms during an attack. Preventive measures can include lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and adequate sleep, and medications, such as beta-blockers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants or painkillers a over-the-counter or prescription drugs, triptans, and anticonvulsants in critical care. If you have migraine, it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to develop an individualised treatment plan that addresses your specific symptoms and triggers.1.3 : Cluster headaches
[caption id="attachment_23943" align="alignnone" width="1024"] hint to get better sleep and reduce stress Fig 1.3[/caption]
hint to get better sleep and reduce stress Fig 1.3[/caption]
Cluster headache is a type of headache characterized by severe recurrent pain in one side of the head, usually around the eyes often described as sharp, burning, or throbbing, and persistent 15 minutes to several hours. Cluster headaches usually occur in cycles, with periods of relief in between.
The causes of cluster headaches are not fully understood, but are believed to be abnormalities in the brain’s hypothalamus, which regulates many bodily functions such as sleep and hormone metabolism. Treatment for cluster headaches may include preventive measures and aggressive treatment to reduce symptoms during an attack. Preventive measures may include lifestyle changes, such as stimulant avoidance and regular sleep schedules, and medications such as verapamil, lithium, and corticosteroids Acute treatment may include oxygen therapy, triptans , or nerve block. If you have cluster headaches, it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses your specific symptoms and triggers. Cluster headaches can be debilitating for many people, but with proper treatment, they can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.Section 2: Causes and Triggers of Headaches
2.1 Lifestyle Factors:
[caption id="attachment_23944" align="alignnone" width="1024"]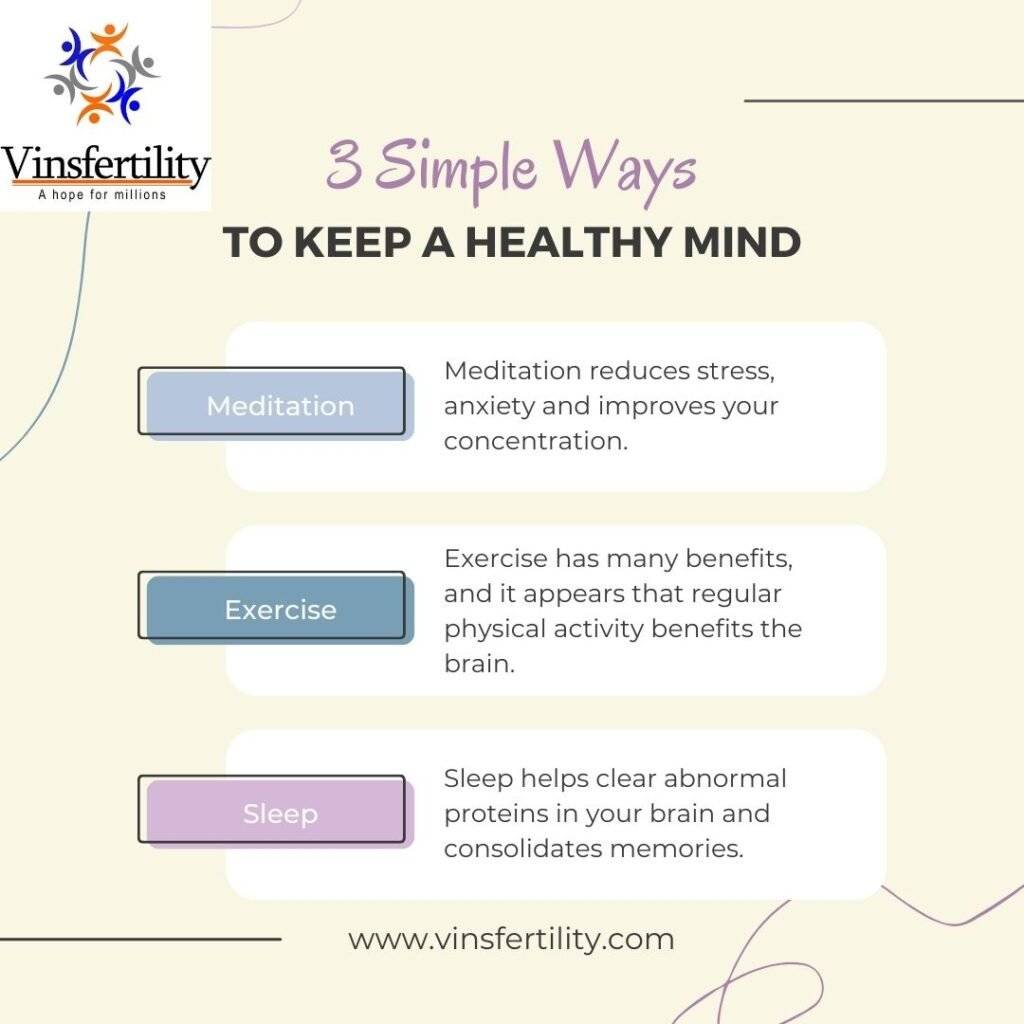 process to keep a healthy mind Fig 2.1[/caption]
Lifestyle factors can play a significant role in the development of headaches. Here are some lifestyle factors that can contribute to headaches:
process to keep a healthy mind Fig 2.1[/caption]
Lifestyle factors can play a significant role in the development of headaches. Here are some lifestyle factors that can contribute to headaches:
- [su_tooltip title="Stress" text="Stress is a mental tension caused by demanding situations. It can lead to anxiety, insomnia, and reduced productivity. Effective management is key." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Stress[/su_tooltip]: High levels of stress can cause headaches and migraines. Stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help manage stress and reduce the frequency and severity of headaches
- [su_tooltip title="Sleet" text="Sleep is vital for health, repairing the body, and brain function. Lack of sleep can impact cognition, mood, and overall well-being." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Sleep[/su_tooltip]: Irregular sleep patterns, sleep deprivation, and oversleeping can all contribute to headaches. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule with the goal of 7-9 hours of sleep per night is recommended.
- [su_tooltip title="Diet" text="A balanced diet fuels the body, supports health, and prevents diseases. It should include fruits, vegetables, proteins, and whole grains. Moderation is key." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Diet[/su_tooltip]: Certain foods and beverages can cause headaches in some people, including caffeine, alcohol and processed foods. Maintaining a balanced diet with plenty of wholesome foods can help reduce the risk of migraines.
- [su_tooltip title="Hydration" text="Hydration is essential for all bodily functions. It aids digestion, nutrient absorption, and detoxification. Drinking enough water daily is vital." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Hydration[/su_tooltip]: Dehydration can cause headaches so it’s important to stay adequately hydrated by drinking water and avoiding excess alcohol or caffeine
- [su_tooltip title="Exercise" text="Exercise promotes overall health, boosts energy, and maintains a healthy weight. It strengthens the heart, improves mood, and enhances mental sharpness." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Exercise[/su_tooltip]: Regular exercise can help reduce stress and improve overall health, which can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. However, exerting too much or exercising too much can also cause headaches, so it’s important to keep a balance.
- [su_tooltip title="Posture" text="Good posture aligns the body correctly, reduces strain on muscles and joints, and promotes overall health. It aids digestion, breathing, and prevents chronic issues." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Posture[/su_tooltip]: Poor posture can cause tension headaches, so it’s important to maintain good posture throughout the day, especially when sitting for long periods of time.
- [su_tooltip title="Eye strain" text="Eye strain can result from prolonged screen time or poor lighting. It leads to headaches, blurred vision, and dry eyes. Regular breaks and proper lighting can help." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Eye strain[/su_tooltip]: Spending too much time staring at a computer or phone can cause eyestrain, which can lead to headaches. Taking regular breaks and adjusting screen brightness can help reduce eye strain.By making lifestyle changes to address these factors, individuals can reduce their risk of headaches and improve their overall quality of life.
2.2 Environmental Triggers:
[su_tooltip title="Environmental stimuli" text="Environmental stimuli, like light, noise, and temperature, can affect mood and productivity. Appropriate management of these factors can enhance comfort and well-being." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Environmental stimuli[/su_tooltip] also play an important role in the development of headaches. Here are some of the environmental stimuli that can cause a headache:
[su_tooltip title="Light" text="Light affects mood, productivity, and sleep. Natural light is best for health. For artificial light, choose warm tones for relaxation, cool tones for focus." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Light[/su_tooltip]: Bright or glaring lights such as sunlight, fluorescent lights, and computer screens can cause headaches. Wearing sunglasses, using anti-glare lenses, or adjusting the brightness and contrast of a computer can help reduce the risk of headaches.
[su_tooltip title="Noise" text="Noise can affect concentration, sleep, and stress levels. While some noise is unavoidable, using earplugs, headphones, or soundproofing can help manage it." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Noise[/su_tooltip]: Loud or frequent noise, such as traffic or construction noise, can cause headaches. Wearing earplugs or noise canceling devices can help reduce the risk of headaches.
[su_tooltip title="smell" text="Smell can influence mood and well-being. Pleasant aromas, like those from essential oils, can reduce stress and improve sleep. Avoid strong, unpleasant odors." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Smell[/su_tooltip]: Strong or unpleasant smells, including cigarette smoke, perfume and chemical fumes can cause headaches. Avoiding exposure to these fragrances or using a mask can help reduce the risk of headaches.
[su_tooltip title="Weather" text="Weather impacts mood, activities, and health. Sunny days can boost mood, while cold, gray ones may lower it. Dress appropriately and take precautions as needed." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Weather[/su_tooltip]: Changes in the weather, including changes in temperature, humidity and wind, can cause headaches. Paying close attention to the weather forecast and avoiding exposure to severe weather can help reduce the risk of headaches.
[su_tooltip title="Allergens" text="Allergens can trigger reactions like sneezing, itching, or asthma. Knowing your triggers and maintaining a clean environment can help reduce exposure and symptoms." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Allergens[/su_tooltip]: Allergens, such as pollen, dust, and allergic pets can cause headaches in some people. Taking steps to reduce allergies, such as using air fresheners or avoiding outdoor activities during peak pollen season, can help reduce risk there to have a headache reduction[su_tooltip title="Physical factors" text="Physical factors like diet, exercise, sleep, and environmental conditions impact health and well-being. Maintaining balance in these can lead to a healthier lifestyle." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Physical factors[/su_tooltip]: Physical factors such as altitude change, jet lag, and motion sickness can also cause headaches. Taking steps to reduce exposure to these physiological factors, such as staying hydrated and drinking excessive amounts of alcohol while traveling on an airplane, can help to reduce risk as a person will have a reduction in headaches
By identifying and avoiding environmental triggers, individuals can reduce their risk of headaches and improve their overall quality of life. It is important to pay attention to individual triggers and take steps to manage them effectively.
2.3 Medical Conditions:
[caption id="attachment_23941" align="alignnone" width="1024"]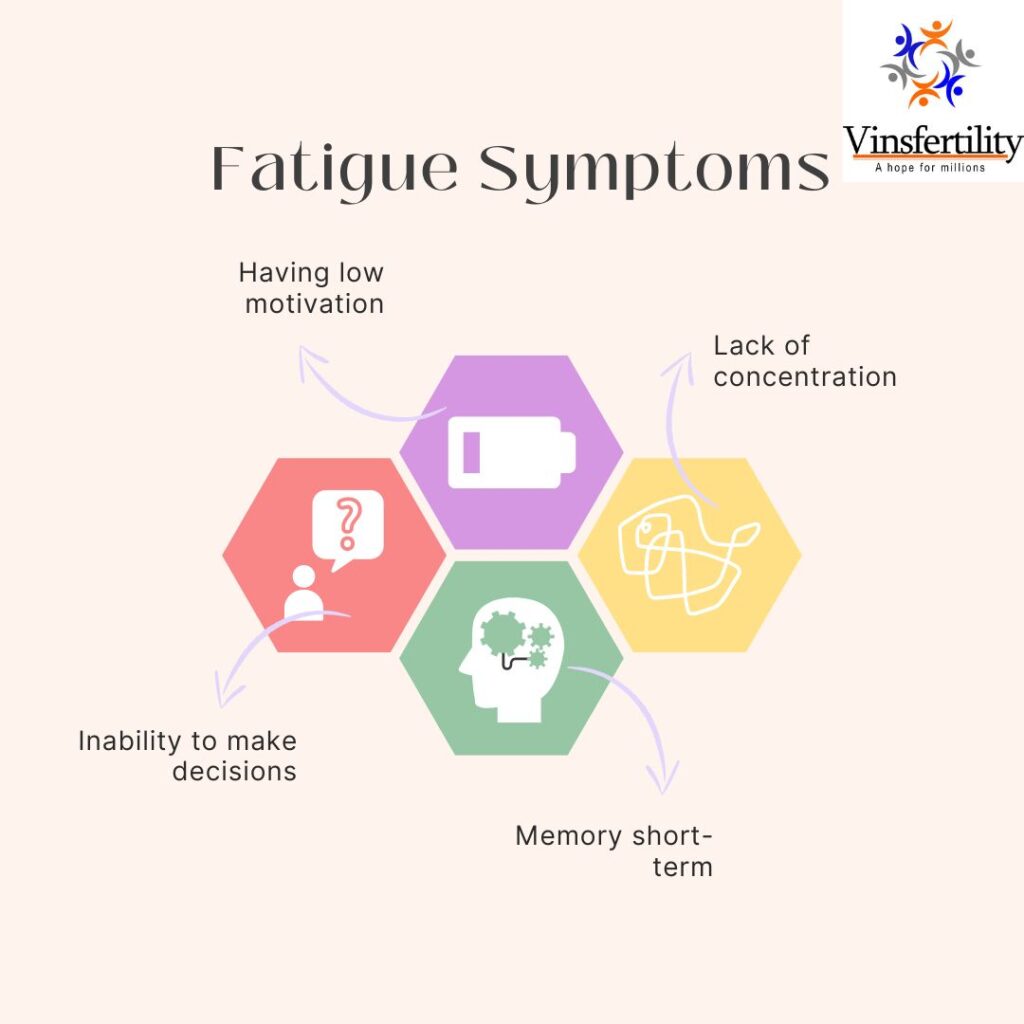 Fatigue Symptoms Fig 2.3[/caption]
Fatigue Symptoms Fig 2.3[/caption]
There are several underlying medical conditions that can cause headaches, some of which include:
[su_tooltip title="Sinus infection" text="A sinus infection causes inflammation and swelling of the sinuses, leading to symptoms like headache, facial pain, and nasal congestion. Rest and proper treatment are key." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Sinus infection[/su_tooltip]: Sinus inflammation or infection can cause sinus headaches.
[su_tooltip title="High blood pressure" text="High blood pressure can strain the heart and damage arteries, leading to serious health issues. Lifestyle changes, diet, exercise, and medication can help manage it." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]High blood pressure[/su_tooltip]: High blood pressure can cause headaches, especially in individuals who are unaware of or unable to control their blood pressure.[su_tooltip title="Hormonal Imbalances" text="Hormonal imbalances can affect mood, metabolism, and reproductive health. They require proper diagnosis and treatment. Lifestyle changes may also help balance hormones." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Hormonal Imbalances[/su_tooltip]: Changes in hormone levels such as during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can cause headaches in some people
[su_tooltip title="Temporomandibular joint" text="Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder causes jaw pain, clicking, and difficulty in jaw movement. Treatment options include medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)[/su_tooltip]: TMJ disorders can cause pain in the jaw and head, which can lead to headaches.
[su_tooltip title="Neck or Spine condition" text=" ChatGPT Neck or spine conditions can cause pain, limited mobility, and discomfort. Treatment options include physical therapy, medication, and in some cases, surgery. Consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Neck or Spine Conditions[/su_tooltip]: Bones in the cervical spine or soft tissue affecting the neck or spine can cause headaches.
[su_tooltip title="Concussion or head injury" text=" Concussion or head injuries can result from a blow to the head, causing symptoms like headache, dizziness, and confusion. Rest, medical evaluation, and gradual return to activities are essential for recovery." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Concussion or head injury[/su_tooltip]: A blow to the head can cause headaches, especially in the days or weeks following the injury.
[su_tooltip title="Brain tumors and other serious medical conditions" text=" Brain tumors and other serious medical conditions require prompt medical attention. Symptoms may include headaches, seizures, cognitive changes, and neurological deficits. Proper diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management are crucial for these conditions. Consult a healthcare professional for guidance." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Brain tumors and other serious medical conditions[/su_tooltip]: While rare, headaches can also be a symptom of more serious medical conditions such as a brain tumor, arthritis, or infection
If the headache is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other troubling symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can help identify the cause of the headache, and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Section 3: Managing and Treating Headaches
3.1 Over-the-Counter Medications:
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can be effective in managing headaches for some individuals. Here are some of the common types of headache medications commonly used to treat headaches.
[su_tooltip title="Acetaminophen" text=" Over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer. Effective for headaches, muscle aches, and fever. Follow recommended dosage." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Acetaminophen[/su_tooltip]: Acetaminophen, like Tylenol, is a pain reliever that can be used to treat mild to moderate headaches. It works by blocking pain signals to the brain.
[su_tooltip title="Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)" text=" NSAIDs: Common pain relievers and anti-inflammatories. Reduce pain, inflammation, and fever. Follow recommended usage and precautions." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"] Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)[/su_tooltip]: NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) are painkillers that can be used to treat mild to moderate headaches they work by reducing inflammation and blocking pain signals to the brain.
[su_tooltip title="Aspirin" text=" Aspirin: NSAID for pain, inflammation, and fever. Also used as a blood thinner. Follow recommended dosage and precautions." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Aspirin[/su_tooltip]: Aspirin is a painkiller that can be used to treat mild to moderate headaches. It works by reducing inflammation and blocking pain signals to the brain.
[su_tooltip title="Drug combinations" text=" Combining drugs: Consult a professional. Interactions and risks can occur. Seek guidance for safe and effective use." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Drug combinations[/su_tooltip]: Combination drugs such as Excedrin are a combination of painkillers, caffeine, and/or antiepileptic drugs, and can be effective in headaches Caffeine can help with pain relief a effectiveness has increased, while anticonvulsants can help reduce inflammation.
It is important to read and follow the instructions on the label of any substance of abuse, and if you have any questions or concerns, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional. It is also important to note that overdoses can lead to recurrent headaches or other health complications, so use these medications only as directed and if headaches are present or internal is severe, it is necessary to consult a clinic to determine the root cause and appropriate treatment.
3.2 Prescription Medications:
For individuals with severe or chronic headaches, prescription medication can be an effective treatment. Here are some common remedies for headaches.
[su_tooltip title="Triptans" text=" Triptans: Effective for migraines and cluster headaches. Constrict blood vessels and block pain pathways. Follow usage instructions and precautions." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Triptans[/su_tooltip]: Triptans are a type of medication used to treat migraines. They work by constricting blood vessels in the brain and reducing inflammation. Triptans are available in oral, oral, and injectable forms.
[su_tooltip title="Ergotamine" text=" Ergotamine: Used for migraines and cluster headaches. Constricts blood vessels. Use under medical guidance. Follow prescribed dosage and precautions." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Ergotamine[/su_tooltip]: Ergotamine is a drug used to treat migraines and cluster headaches. They work by constricting blood vessels in the brain. Ergotamines are available for both oral and rectal use.
[su_tooltip title="Calcium channel blockers" text=" Calcium channel blockers: Medications that relax blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and treating conditions like hypertension and angina. Use as directed and consult a healthcare professional." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Calcium channel blockers[/su_tooltip]: Calcium channel blockers are a type of medication used to treat cluster headaches. They work by relaxing blood vessels and reducing inflammation.
[su_tooltip title="Calcium channel blockers" text=" Antidepressants: Medications used to treat depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. Consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Antidepressants[/su_tooltip]: Certain types of antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be used as prophylaxis to reduce headache frequency and severity den the snow
[su_tooltip title="Anticonvulsants" text=" Anticonvulsants: Medications used to treat seizures and epilepsy. They may also be used for mood disorders and neuropathic pain. Follow medical advice." background="#fb7700" color="#201c14"]Anticonvulsants[/su_tooltip]: Certain anticonvulsants, such as topiramate and valproic acid, can also be used as prophylaxis to reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
It is important to consult with a health care professional to determine which medications and dosages are appropriate for your specific condition. It is also important to follow your healthcare professional’s instructions and prescriptions, and to report any problems or concerns to your healthcare professional.
3.3 Non-Pharmacological Treatments:
Non-drug treatments can be an effective way to manage headaches, especially for individuals who prefer to avoid medications or do not find their medications effective Here are some common non-drug treatments for headaches . . . .
Relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, and slow muscle relaxation can be effective in reducing stress and tension, and can be helpful relieve the headache
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific areas on the body, and can be effective in controlling the frequency and severity of headaches
Biofeedback: Biofeedback uses electronic sensors to monitor and train the body’s response to stress, which can be effective in controlling the frequency and severity of headaches
Massage: Massage can be effective in reducing muscle tension and relaxing, which can help relieve headaches.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of treatment that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors, and can be effective in reducing stress and tension, and can help relieve headaches
It is important to speak with a health care professional to determine the appropriate non-drug treatment for your specific condition. It's also important to keep in mind that some non-drug treatments might not be covered by insurance, so it's crucial to check with your insurance company about coverage.
3.4 Lifestyle Changes:
Making the right lifestyle changes can be an effective way to reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Here are some lifestyle changes that can help manage headaches:
Exercise regularly: Exercising regularly can help reduce stress and tension, which can help relieve painful headaches. It is important to start slowly and increase the intensity gradually to avoid triggering headaches.
Adequate sleep: Regular and adequate sleep is important for overall health and can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule with the goal of 7-9 hours of sleep per night is recommended.
Stress management: Stress is a common trigger for headaches, so it’s important to use stress management techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to help reduce stress and tension
Stay hydrated: Dehydration can cause headaches, so it’s important to stay adequately hydrated by drinking water and avoiding too much alcohol or caffeine
Healthy diet: Maintaining a balanced diet with plenty of wholesome foods can help reduce the risk of migraines. Certain foods and beverages, such as processed foods, caffeine and alcohol, can cause headaches in some individuals.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of headaches and improve their overall quality of life. Lifestyle changes take time and individual experimentation to find effective strategies for each person's needs.Section 4: There are several preventive measures that can be taken to reduce the frequency and severity of headaches, regardless of the type of headache. These may include:
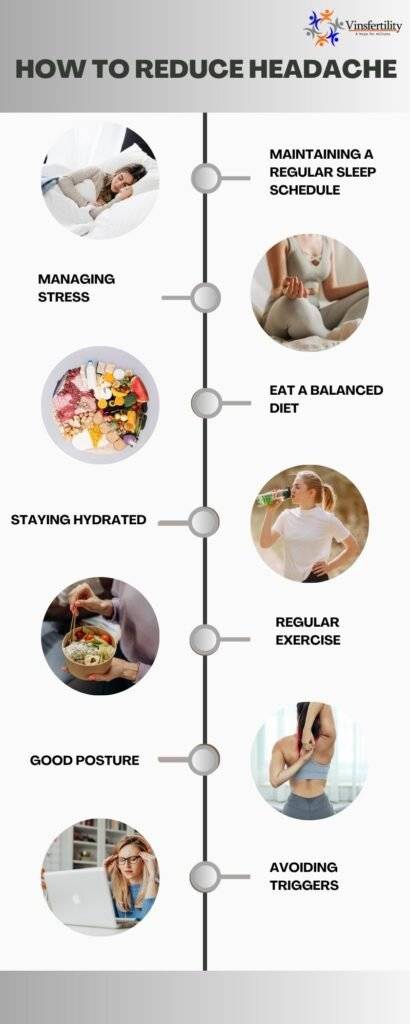 process to reduce headache.Fig.4.0[/caption]
process to reduce headache.Fig.4.0[/caption]
-
Maintaining a routine: Getting enough sleep and staying asleep regularly can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
Managing Stress: Stress is a common trigger for many types of headaches. Stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and reduce the frequency of headachesEating a balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet and avoiding trigger foods can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Stimulants can vary from person to person, but common ones include chocolate, caffeine and alcohol.
Stay hydrated: Dehydration can be a trigger for some headaches. Drinking enough water and staying hydrated can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
Regular exercise: Exercising regularly can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. To avoid triggering headaches, it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the exercise.
Good posture: Good posture relieves muscle tension and headaches. Proper posture throughout the day, especially when sitting at a desk, can help reduce the frequency of headaches.
Avoiding triggers: Like certain foods, bright lights, or strong smells, identifying and avoiding potential triggers can be an effective way to reduce headaches frequency and severity
Collaborate with a healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan targeting your symptoms and triggers.
Section 5 : There are several alternative and complementary therapies that can be used to manage headaches. These may include:
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific areas on the body. It has been found to be effective in controlling the frequency and severity of headaches.
Massage: Massage can help relieve muscle tension and improve blood circulation, which can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches
Chiropractic care: Chiropractic care involves adjustments to the spine and other joints to reduce pain and improve function. It may help to deal with certain types of headaches, such as migraines.
Herbal Remedies: Certain herbal remedies, such as fever and butter, have been found to be effective in controlling the frequency and severity of migraines
Mind-body techniques: Mind-body techniques such as meditation, yoga, and biofeedback can help reduce stress and improve relaxation, which can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches
Cognitive-behavioral therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that can contribute to headaches.
Use alternative medicine as a complement to conventional treatments; consult your healthcare provider for safety and effectiveness.
Section 6 : Here are a few real-life stories of people who have suffered from headaches and how they have managed their symptoms:
- Laura: Laura suffered from migraines for years, triggered by stress and certain foods. Despite trying various drugs, they failed. She eventually found relief through regular exercise and yoga. These treatments reduced stress and improved her posture, as well as reducing the frequency and severity of her migraines.
- John: John suffered from migraine headaches due to his poor posture and his stress from work. When she sought help, she began seeing a physical therapist who provided postural guidance and taught stress-reducing exercises. By incorporating mindfulness, John successfully managed stress and reduced the frequency and severity of his headaches.
- Sarah: Cluster headaches plague Sarah, triggered by climate change and specific foods. Despite unsuccessful attempts to take medication, exercise provided relief, which reduced her frequent and severe headaches. Sarah made further dietary changes, avoiding stimulants, which again helped with symptom relief.
- Mike: Mike dealt with chronic headaches on a daily basis stemming from stress and poor sleep patterns. Her journey to recovery included seeing a psychologist, who helped manage stress and improve sleep. The addition of daily prophylaxis significantly reduced the frequency and severity of her headaches.
Section 7: When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Consult a healthcare professional for headaches. Early detection and treatment of underlying conditions can prevent complications. 7.1 Signs of a Serious Underlying Condition If your headache is accompanied by any of the following symptoms, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately: a) Sudden and severe headache, unlike any you've experienced before b) Stiff neck, fever, and/or rash, which could indicate meningitis c) Headache following a head injury or trauma d) Difficulty speaking, vision changes, or weakness on one side of the body, which may be signs of a stroke e) Seizures or loss of consciousness These symptoms could signal a more serious medical issue that requires prompt evaluation and treatment. 7.2 Persistent or Worsening Headaches If you're experiencing persistent headaches that don't improve over time or are worsening in severity, it's important to consult a healthcare professional. This could indicate an underlying issue, such as chronic tension headaches, migraines, or other medical conditions that require specific treatment plans. 7.3 Ineffective Home Treatments If you've tried various home remedies and over-the-counter medications without relief, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional. They can help determine the cause of your headaches and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include prescription medications, alternative therapies, or lifestyle changes.Conclusion:
FAQ: Headache - Understanding Causes, Types, and Relief Strategies
Q1: What are the main types of headaches?
Ans: The main types of headaches are tension headaches, migraines, and cluster headaches. Tension headaches are the most common, characterized by a dull, aching pain, while migraines are more severe and often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Cluster headaches are extremely painful but rare, typically occurring on one side of the head.Q2: What causes headaches?
Ans: Factors like poor sleep, stress, dehydration, skipped meals, and environmental triggers can contribute to headaches. In addition, underlying medical conditions such as sinus infections, high blood pressure, or hormonal imbalances can play a role.Q3: How can I treat a headache?
Ans: Treatment options for headaches vary depending on type and severity. For mild to moderate pain, over-the-counter pain relievers like aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen can provide relief. In cases of severe or chronic headaches, prescription or preventative medications may be needed. Non-pharmacological approaches, including relaxation techniques, acupuncture, biofeedback, or massage therapy, can also be beneficial in managing headache pain.Q4: How can I prevent headaches?
Ans: Prevent headaches with lifestyle changes: exercise, sleep, stress management, hydration, balanced diet, trigger avoidance.Q5: When should I see a doctor for my headaches?
Ans: You should consult a healthcare professional if your headaches are severe, persistent, or worsening over time; if they interfere with your daily activities; or if you experience additional symptoms such as fever, stiff neck, or vision changes. Your doctor can help determine the cause of your headaches and recommend appropriate treatment options.Q6: Can headaches be a sign of a more serious medical condition?
Ans: Seek medical advice for severe, sudden, or changing headache patterns or if accompanied by concerning symptoms. Sources :- Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/headache/basics/causes/sym-20050800
- National Headache Foundation: https://headaches.org/
- American Migraine Foundation: https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/resource-library/
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Headache-Information-Page
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: https://www.cdc.gov/headache/index.html
- World Health Organization - Headache Disorders (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/headache-disorders)
- Cleveland Clinic - Headaches (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9639-headaches)


